_replaceDesigningreplaceforoice-EnabledreplaceWebreplaceExperiences.png)
- July 31, 2023
- 127 Views
Imagine a world where you can speak your thoughts and desires, and the digital realm responds promptly, seamlessly integrating into your daily life.
Whether you want to search for information, control smart home devices, order groceries, or even book a ride, the voice is becoming the conduit that effortlessly bridges the gap between humans and machines.
Designing for voice-enabled web experiences requires a deep understanding of how humans communicate, think, and interact. It involves crafting user interfaces that are not limited to visual elements but extend to the power of speech.
In this blog, we will explore the intricacies of VUI design and dive into the best practices, techniques, and considerations that go into creating exceptional voice-enabled web experiences.
-
Table of Contents
-
- 1. Overview of Voice-Enabled Web Experiences
- 2. Importance of Voice-Enabled Web Experience
- 3. Benefits of VUI Design
- 4. Challenges of VUI Design
- 5. Key Concepts in VUI Design
- 6. Designing for Voice-Enabled Web Experiences
- 7. Technical Considerations for VUI Design
- 8. Future Trends in VUI Design
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. FAQs
-
Overview of Voice-Enabled Web Experiences
Voice-Enabled Web Experiences refer to the use of voice as a primary interface for interacting with web-based applications and services. It allows users to interact with websites, web applications, and other online platforms using natural language and voice commands instead of traditional text-based input. With the proliferation of voice assistants and smart speakers, voice-enabled interactions have become increasingly popular and are transforming the way users engage with technology.
Importance of Voice-Enabled Web Experience
- Accessibility: Voice-Enabled Web Experiences make technology more accessible to a wider range of users, including those with visual impairments, physical disabilities, or individuals who struggle with traditional keyboard input. It enables a more inclusive experience for all users.
- Convenience and Efficiency: Voice interactions can be faster and more convenient than typing, especially in scenarios where users are multitasking or have limited mobility. Voice commands enable users to perform tasks hands-free and get immediate responses.
- Natural and Intuitive: Voice is a natural mode of communication for humans, and voice-enabled experiences provide a more intuitive and user-friendly interface. It reduces the learning curve associated with complex user interfaces and enables a more natural interaction paradigm.
- Contextual and Personalized: Voice assistants can leverage user data and context to provide personalized experiences. By analyzing user preferences, history, and contextual information, voice-enabled systems can deliver customized recommendations, content, and services.
- Multimodal Experience: Voice-enabled interfaces can be combined with other modalities, such as visual displays or haptic feedback, to create a rich and immersive user experience. This allows for more flexible and adaptable interactions in different environments and across various devices.
Benefits of VUI Design
- Enhanced User Experience: Voice interactions provide a more intuitive, natural, and conversational interface, resulting in a better user experience. It can simplify complex tasks, reduce cognitive load, and make interactions more engaging and interactive.
- Increased Accessibility: Voice-enabled interfaces make technology accessible to a wider audience, including individuals with disabilities or those who have difficulty with traditional input methods.
- Hands-free and Multitasking: Voice commands allow users to perform tasks and access information without using their hands, enabling multitasking and convenience in various scenarios, such as cooking, driving, or exercising.
- Personalization and Contextualization: VUI design can leverage user data and contextual information to deliver personalized experiences, recommendations, and content tailored to the user's preferences and needs.
Challenges of VUI Design
Key Concepts in VUI Design
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): NLU involves the ability of a voice-enabled system to accurately understand and interpret user input, including the intent and context behind the spoken commands or queries.
- Dialog Management: Dialog management focuses on designing conversational flows and interactions between the user and the voice-enabled system. It involves handling turn-taking, managing context, and guiding the user through the conversation.
- Voice User Interface (VUI) Prototyping: VUI prototyping involves creating interactive prototypes of voice-enabled systems to test and refine the user experience. It helps designers and developers visualize and iterate on the voice interactions before implementation.
- Persona and Voice Tone: VUI design often involves defining the persona and voice tone of the voice-enabled system. The persona represents the system's personality and characteristics, while the voice tone reflects the style and manner of communication.
- Error Handling and Recovery: Effective error handling is crucial in VUI design to guide users when they make mistakes or encounter errors. Designers need to anticipate potential errors, provide clear error messages, and offer suggestions for recovery.
- Multimodal Design: Multimodal design involves integrating voice interactions with other modalities, such as visual displays or tactile feedback, to create a cohesive and seamless user experience. It requires careful consideration of how different modalities complement each other.
Designing for Voice-Enabled Web Experiences
A. User-Centered Design Approach
- User Research and Personas: User research involves gathering insights about the target users, their needs, preferences, and pain points when interacting with voice-enabled web experiences. Personas are fictional representations of different user types that help designers empathize with and design for specific user groups.
- User Journey Mapping: User journey mapping visualizes the user's end-to-end experience with the voice-enabled web experience, identifying touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. It helps designers understand the user's goals, context, and interactions at each stage.
- Voice User Flows: Voice user flows outline the sequence of steps and interactions between the user and the voice-enabled system. It focuses on designing the conversational flow, including prompts, user responses, system actions, and error handling.
B. Content Design and Information Architecture
- Adapting Content for Voice Interaction: Content designed for voice interactions should be concise, conversational, and easily spoken aloud. It requires adapting written content for spoken delivery, considering factors like natural language, pacing, and readability for voice output.
- Structuring Conversational Content: Conversational content should be structured logically, using a hierarchical approach to ensure clarity and ease of understanding. Breaking down complex information into smaller, contextually relevant chunks enhances the user's comprehension and reduces cognitive load.
- Navigation and Command Design: Voice interfaces require intuitive and user-friendly navigation and command design. Designers should create clear and intuitive navigation structures and define easy-to-understand voice commands to enable users to access specific features or content.
C. Voice Interaction Design Principles
- Clear and Concise Dialogue: Voice interactions should be designed to be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoiding jargon, using simple language, and providing relevant information help users comprehend and engage with the voice-enabled system effectively.
- Error Handling and Recovery: Effective error handling is crucial in voice interactions. Designers should anticipate potential errors and provide clear error messages, prompts for correction, and suggestions for alternative actions to help users recover from mistakes.
- Feedback and Confirmation: Providing feedback and confirmation during voice interactions is essential to reassure users and maintain their trust. Auditory cues, such as voice prompts or confirmation sounds, can indicate system responsiveness and validate user actions.
- Personalization and Contextualization: Designing for personalization and contextualization involves leveraging user data and preferences to deliver customized experiences. Tailoring the content, recommendations, and responses based on the user's history and context enhances the overall user experience.
D. Multimodal Experiences
- Combining Voice with Visual Elements: Multimodal experiences integrate voice interactions with visual elements, such as text, images, or graphical interfaces. Designers should ensure visual elements complement and enhance the voice interactions, providing additional context, feedback, or supplementary information.
- Adapting for Different Devices and Platforms: Voice-enabled web experiences should be designed to work seamlessly across different devices and platforms. Consideration should be given to varying screen sizes, input capabilities, and interaction patterns to provide a consistent and optimized experience.
- Handling Interruptions and Transitions: Voice interactions should be designed to handle interruptions or transitions smoothly. Users may pause, switch devices, or receive external notifications during an interaction. Designers should consider how the voice-enabled system handles these interruptions and seamlessly resumes the interaction. x
Technical Considerations for VUI Design
- Speech Recognition and NLP Technologies: VUI design relies on speech recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies to accurately interpret user input. Designers should understand the capabilities and limitations of these technologies to optimize the design and ensure reliable voice recognition.
- Integrating Voice Assistants and APIs: Voice-enabled web experiences often integrate with voice assistant platforms and APIs. Designers should be familiar with the integration requirements and guidelines to create seamless and interoperable experiences.
- Accessibility and Inclusive Design: Ensuring accessibility and inclusive design is crucial for voice-enabled web experiences. Designers should consider accessibility standards, provide alternative input methods, and ensure that voice interactions are accessible to users with disabilities.
- Performance Optimization for Voice Interfaces: Optimizing the performance of voice interfaces is essential for a smooth user experience. Designers should consider factors like response time, latency, and system efficiency to minimize delays and ensure real-time interactions.
- Privacy and Security Considerations: Voice interactions involve processing sensitive user data, so privacy and security should be prioritized. Designers should follow best practices for data protection, secure communication channels, and obtain user consent for data collection and usage.
Future Trends in VUI Design
Voice-Enabled Web Experiences and VUI design are continuously evolving fields. Here are some future trends to watch for:
- Emotion Detection and Sentiment Analysis: Voice-enabled systems may incorporate emotion detection and sentiment analysis to better understand user emotions and tailor responses accordingly. This could enable more personalized and empathetic interactions.
- Improved Natural Language Understanding (NLU): NLU technology is expected to advance, allowing voice-enabled systems to better understand complex queries, handle ambiguity, and provide more accurate responses.
- Multi-turn Conversations: Voice interactions may evolve to support more complex multi-turn conversations. This would enable users to have extended dialogues and perform intricate tasks with the voice-enabled system.
- Integration with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Voice interactions can be combined with AR and VR technologies to create immersive and interactive experiences. Users may navigate virtual environments and interact with objects using voice commands.
- Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT): Voice-enabled systems can integrate with IoT devices, allowing users to control and interact with their smart homes, appliances, and other connected devices using voice commands.
- Voice Commerce: Voice-enabled systems are likely to play a significant role in voice commerce, enabling users to make purchases, place orders, and conduct transactions using voice commands.
Conclusion
Voice-enabled web experiences and VUI design offer tremendous potential for web development companies to create innovative and engaging user interfaces. This can help businesses drive growth and enhance user satisfaction.
With a focus on user-centric design, continuous learning, and strategic partnerships, you can unlock the full potential of this exciting technology and drive business growth for your app development company.
FAQs
What is an example of a voice user interface VUI?
An example of a voice user interface (VUI) is Amazon's voice assistant, Alexa, which allows users to interact with various smart devices using voice commands and natural language.
What is the goal of building system personas for voice user interface design?
The purpose of creating system personas for VUI design is to understand the target users and their characteristics, preferences, and needs. Personas help designers empathize with users, tailor voice interactions to their requirements, and create more personalized and effective experiences.
Which utilities are used in the design of VUI?
Some tools used in the design of voice user interfaces include Dialogflow, Alexa Skills Kit, Bixby Developer Studio, and Watson Assistant. These tools provide platforms and frameworks for designing, building, and testing voice interactions and integrations with voice assistant platforms.
About Author
You May Also Like

The food delivery application has innovative, game-changing features that will transform the industry from the bottom to the top. According to Statista, the online food delivery market in the UAE has

An extensive background working in Tech, Travel, and Education Industries. Currently involved in entire business operations process: Benefits strategy and implementation, systems integration, Human Re
The healthcare industry is one of the most rapidly changing and growing industries worldwide. Mobile devices and apps have drastically changed how providers and patients interact and communicate.So, i

If you’re planning to enter the fast-growing fantasy sports market, one of the most critical aspects considered is “What will it cost to build a fantasy sport that stands out and drives t

Rental businesses are gaining market share by offering essential services that help other businesses minimize downtime and maximize profitability. This growth trend is particularly strong in the servi

The two hottest frameworks in the mobile app development world are Flutter and React Native. They’re both cross-platform solutions that allow you to write code once and deploy it to Android and

When it comes to developing an app, there's a lot to consider. Not only do you need to create a user-friendly interface and design, but you also need to make sure your app is able to meet the demands

When it comes to mobile app development, one of the most important things you need to consider is the prototyping process. This will allow you to create a working model of your app so that you can tes

Have you ever found yourself in a situation where you desperately needed a product or service but didn't have the time or energy to go out and get it? Well, fear no more because on-demand delivery app

As blockchain technology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of projects built on its foundation. The worldwide Blockchain market is predicted to expand at a CAGR of 42.8% (2018-2023), dire

Building an App that promotes businesses and acts as a right hand has a separate fanbase! Creating an app for the business plays a fundamental role in elevating business operations, making seamless c

Will DeepSeek and ChatGPT collide in the race for AI Supremacy? DeepSeek and ChatGPT are at the center of a heated debate that tends to shape the future of AI. The real-world implications and effecti

Hiring a team of remote developers can be a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. With a little bit of planning and the right approach, you can find the perfect candidates to build your dream prod

Things have changed dramatically over the years with new opportunities, techniques, and future advancements. Real estate is the best industry to invest in, though the procedure sometimes irritates. Me

With the advent of technology, the financial industry has experienced a massive transformation in the past few years. Fintech applications have revolutionized the way we manage and invest our money.

Blockchain iѕ a technology that enables thе creation оf digital property with a secure record оf ownership. It’ѕ the backbone of Bitcoin, thе firѕt аnd most well-known cryptocurrency. B

Having a mobile application is no longer a luxury—it's an essential tool for instantly capturing the market! To stand out in the rental businesses, a company must adopt tech-driven preferences

The gaming industry is proliferating with the advent of smartphones and PCs. Every age group, from children to adults, is well-engaged and fond of online gaming. The rapid evolution of mobile gaming a

Picture this: a world where traditional banking transforms into a cutting-edge, efficient, and transparent system that leaves everyone in awe. Blockchain, often met with skepticism and uncertainty, is

You’ve likely heard the term “Artificial Intelligence” or AI until now—It’s 2025. But have you ever paused to consider how deeply AI has woven itself into the web of our

DeFi is a new kind of investment that’s taking the world by storm. So what is it? Essentially, DeFi is a digital asset class that allows you to invest in cryptocurrencies and other digital asset

By 2024, we all know that technology will be the future. What excites me the most is that technology has covered all the dimensions of businesses, enabling them to attain their potential and efficienc

Lately, the tech world has been abuzz with talk of the Metaverse, a groundbreaking concept that promises a shared virtual space where people can interact and engage with one another. This futuristic i

Over-the-top (OTT) platforms like Disney Plus, Netflix, and Prime Video have gradually captured attention as traditional TV-watching methods have faded. Throughout the year, OTT platforms have created

Table of Contents 1. What is ChatGPT? 2. What Are the Top Benefits of ChatGPT? 3. How Does ChatGPT Work? 4. Challenges With ChatGPT 5. ChatGPT and the Future of AI 6. Final Thoug

The mobile app market has grown to a staggering size, with over 1.8 million apps available in the Google Play Store and Apple App Store combined. Mobile apps have become a necessity for people worldwi

Blockchain technology and web development are two powerful innovations that have the potential to transform our world. While they may appear distinct, they share similarities and can work together to

As the world of startups becomes increasingly competitive, building an MVP is crucial for entrepreneurs looking to test their ideas and launch successful businesses. By creating a minimum viable prod
_replaceDesigningreplaceforoice-EnabledreplaceWebreplaceExperiences.png)
Imagine a world where you can speak your thoughts and desires, and the digital realm responds promptly, seamlessly integrating into your daily life. Whether you want to search for information, contro

Do you want to build a simple app for your business? Do you want to create an app that enhances the experience of users who play games on their smartphones? Whatever your reason, I have created this g

Mobile applications play a vital role in the development of multiple businesses in this digital world. Most companies are investing in iOS app development to strengthen their market appearance and dra

Picture this - a world where business transactions are seamless, secure, and transparent. This might have seemed like a distant dream before the advent of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, b

Social media apps are all the rage these days. People use them to connect with friends and family, to learn about new products and services, and to stay up-to-date on the latest news. But as popular a

Mobile app development is quickly becoming a necessity for businesses. As the world becomes increasingly digital, companies of all sizes rely on mobile apps to reach customers and increase customer en

Can you give thought to a week without coffee breaks at cafes? It might not be possible, but earlier, having coffee outside the house was never a thing. So how the tables have changed the corners?

In today's digital world, businesses must keep up with ever-increasing consumer expectations and find new ways to engage their audience. That's where Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) come in. PWAs are a r

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is flourishing as the hub for blockchain technologies, transforming the digital ecosystem and having a forward-thinking government to maintain its competitive edge. Gove

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a modern and evolving region of finance that is less centralized and more open to innovation and collaboration. DeFi enthusiasts laud its prospect of disrupting convent

Nowadays, the digital presence has revolutionized business dynamics. App development is not just evolving but breaking traditional barriers and emerging as strong and progressive solutions. With robus

Do you run your own business and want to build an Android app? If yes, you must know about the latest technology trends playing a significant role in the android app development process. Technology i

Google released Android 13 beta 4 to the public, and with it comes a slew of new features and updates. In this article, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about the latest version of A

Prime Minister Narendra Modi eventually launched 5G in India at the 6th edition of the IMC (India Mobile Congress). Reliance Jio and other telecom organizations documented the various use cases of 5G

In recent years, the gaming industry has seen a surge in popularity, with many gamers turning to online gaming platforms and console games in order to escape reality. With so many people playing video

Are you aware that the world is going through a significant shift in the way we make payments? According to a recent report by Deloitte, the total value of digital payments worldwide is estimated to r

IPTV has established itself as a prominent technology that is gaining traction with its comprehensive platform applications. Unlike traditional methods like satellite, cable, or TV, IPTV has accelera

The launch of Node.js 19 is now available! It substitutes Node.js 18 as the current launch line, with Node.js 18 being encouraged to long-term support (LTS) next week. What do these two launches mean
The beacon technology market was valued at 519.6 million U.S. dollars in 2016, and it was estimated to increase at a CAGR of 59.8% to reach about 56.6 billion U.S. dollars in size in 2026. Throughout

Imagine a classroom where history comes alive in the 3D model of historical events. Biology students can explore the unique complexities of a cell as they have practiced it with real-world examples, a

The rise of online video streaming services has revolutionized the entertainment industry, prompting businesses worldwide to explore the possibility of launching their own platforms. With giants like

Generative AI? Is this still a question mark to you? If you don’t know what generative AI does, that would be a fair question, but it was not if you said that you haven’t interacted with

The world of gaming is rapidly evolving, and the latest buzzword is "metaverse." The term refers to a virtual world where users can interact with each other and digital objects in real time, using imm

Application development is essential to fostering business efficiency while accepting new changes. Depending on the specific requirements, 85% of businesses rely on software development solutions to s

Table of Contents 1. What is Flutter? 2. Why Choose Cross-Platform Development? 3. Why is Flutter the Best Platform to Make Cross-platform Applications? 4. How Much Does it Cost to

With the ubiquity of smartphones and tablets, it only makes sense that mobile app development - which is the process of creating applications for smartphones and tablet devices - is becoming more popu

In the last few years, wearables have become increasingly popular. Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and even smart glasses are becoming more and more commonplace. And as the technology improves and bec

Businesses after COVID are going through several changes, and the food industry is no different. Restaurants that have been doing dine-in are now struggling to keep up with the demand for delivery and
The introduction of online payment applications has changed how people perform financial transactions. A mobile phone with a banking app lets you quickly resolve various financial matters.

Nowadays, the financial industry has encountered massive digitization, and mobile apps play a significant role in it. There are a wide variety of money transfer apps available, catering to the needs a

Technology has come a long way in the past decade, and augmented reality (AR) is one of the most exciting development fields. AR technology superimposes digital content into the real world, creating a

Do you know what digital transformation with AI is and how it can impact your business? Organizations today are under pressure to digitally transform to stay competitive. This digital transformation

Mobile applications have dominated the market, helping businesses to reinforce their full potential. Not only for the rental business, but mobile apps play a critical role in establishing a solid foun

Want to establish a new business or improve an existing one? You should consider using blockchain technology Being a distributed database, Blockchain allows for secure online transactions. This techn

It's no secret that the digital world has transformed many aspects of our lives, and it is only going to continue changing in ways we can't even imagine yet. To help businesses keep up with this rapid

Businesses these days are looking to have an edge over their competition by having a strong online presence. A website is not enough anymore, and many companies are turning to mobile apps as a way to
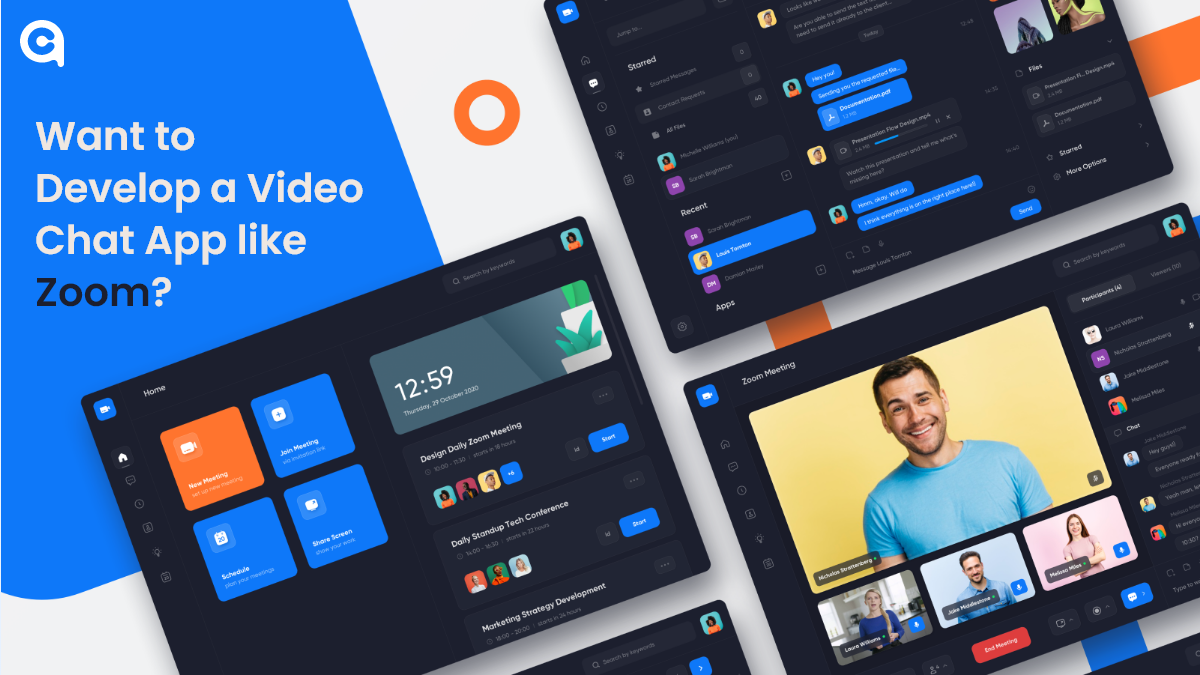
Depending on what niche you’re in, video chat apps are becoming increasingly common in the world of business and technology. Whether it’s a small startup company or a multinational corpora

Are you looking to design a mobile app in 2025? Mobile application development is an ever-changing field, and it can be hard to keep up with the latest trends and best practices. But with this guide,

Blockchain technology is becoming the heart of multiple industries. It is robustly securing businesses through its core value, making it the first pick-up in the generative AIs. The blockchain is the

If you’re in the healthcare industry, then you know that data privacy and security are of utmost importance. In order to protect patients’ information, the Health Insurance Portability and

Blockchain technology has been a hot topic recently due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that ensures transparency, security, and dec

Gone are the days when people used to wave down a taxi on the street or wait for one at the airport. With the advent of technology, people can now book a taxi with just a few taps on their smartphones

As we head into the future, more and more people are looking to find ways to improve their healthcare. And with good reason - healthcare can be expensive, and it can be difficult to get the right care

Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are the two leading buzzwords in the technology era. What began as a completely new, significantly different technology has rapidly revolutionized into something

Did you know that Dubai's prime residential market is projected to experience the world's strongest growth in 2025? The Middle East is buzzing with opportunities, especially in the realm of mobile app
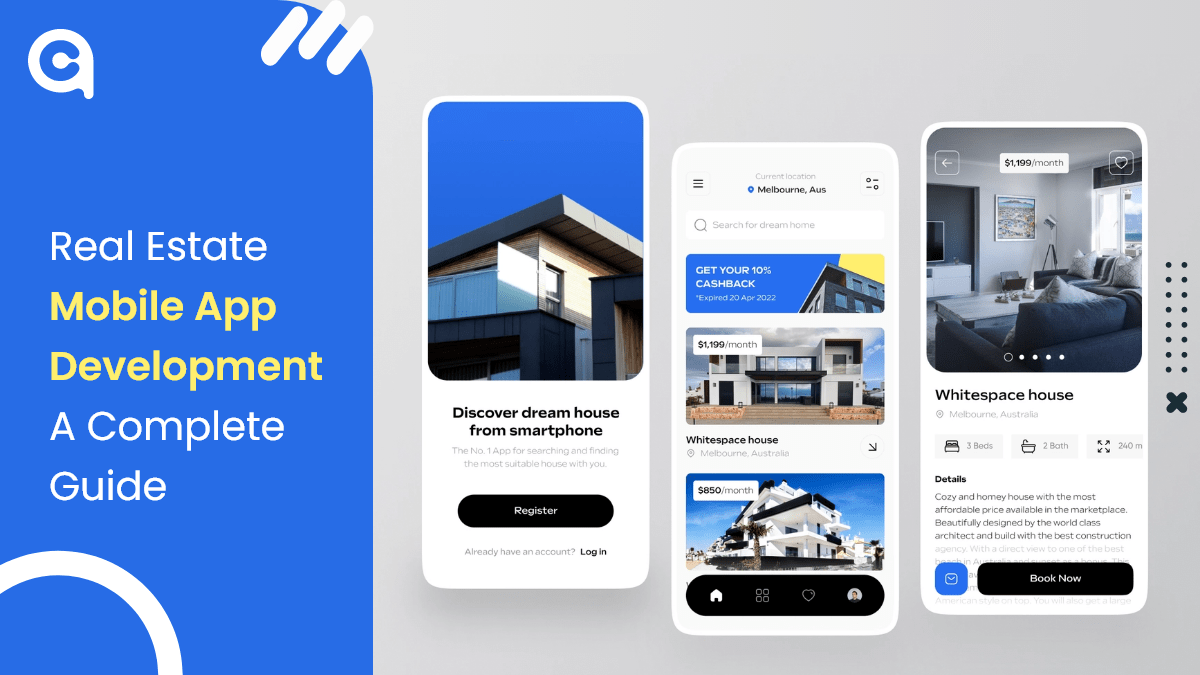
The world is digitizing at a very rapid pace, and in such a scenario, real estate businesses must also go digital to stay ahead of the competition. One of the best ways to digitize your business is de

Is your business still relying on off-the-shelf software solutions that don’t efficiently meet your unique business requirements? If your mind instantly says yes, then let’s explore why in

Over the past decades, the healthcare sector has continuously expanded its wings, moving from traditional to advanced technological processes. This evolution is driven by the sector's unwavering commi
Have you ever felt like you’ve attracted 30% more consumers to your shopping sales by using a technical hack to revive your shops? It would work like a person was crossing through next to your
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be publishedDO YOU HAVE ANY PROJECT
Let's Talk About Business Solutions With Us
India Address
57A, 4th Floor, E Block, Sector 63, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
Call Us
+91 853 500 8008
Email ID
[email protected]